

When a staining agent is used in the lab, bacteria can be classified as “gram negative” or “gram positive.” The staining agent attaches to the bacteria’s cell walls. Many anaerobic bacteria are found in the intestines of animals and are associated with manure and bad smells (Lowenfels & Lewis, 2006). Many pathogenic bacteria prefer anaerobic soil conditions and are known to outcompete or kill off aerobic bacteria in the soil. Anaerobic bacteria are generally found in compacted soil, deep inside soil particles (microsites), and hydric soils where oxygen is limiting. Examples of aerobic bacteria include the Aerobacter genus which is widely distributed in the soil and actinomycetes bacteria genus Streptomyces which give soil its good “earthy” smell (Lowenfels & Lewis, 2006).Īnaerobic bacteria prefer and some require an environment without oxygen. Most soil bacteria prefer well-oxygenated soils and are called aerobic bacteria and use the oxygen to decompose most carbon compounds. Soil oxygen levels often determine soil bacteria activity (Dick, W., 2009). Most microbes are generally inactive and may only have short burst of soil activity. Classifying bacteria by shape is complex because many bacteria have different shapes and different arrangements. Actinomycetes are still classified as bacteria but are similar to fungi except they are smaller in size. Bacteria generally have three major shapes: rod, sphere or spiral. When scientists started first classifying bacteria, they started by looking at their basic shape. Most bacteria are classified into one of the following four categories. Flourishing microbial populations increase soil productivity and crop yields over time. Bacteria population may easily double in 15-30 minutes. Since bacteria live under starvation conditions or soil water stress, they reproduce quickly when optimal water, food, and environmental conditions occur. Bacteria are so simple in structure that they have often been called a bag of enzymes and/or soluble bags of fertilizer (Dick, R., 2009). Most soils are simply a graveyard for dead bacteria cells. Bacteria’s small size enables them to grow and adapt more rapidly to changing environmental conditions than larger, more complex microorganisms like fungi. They grow and live in thin water films around soil particles and near roots in an area called the rhizosphere.
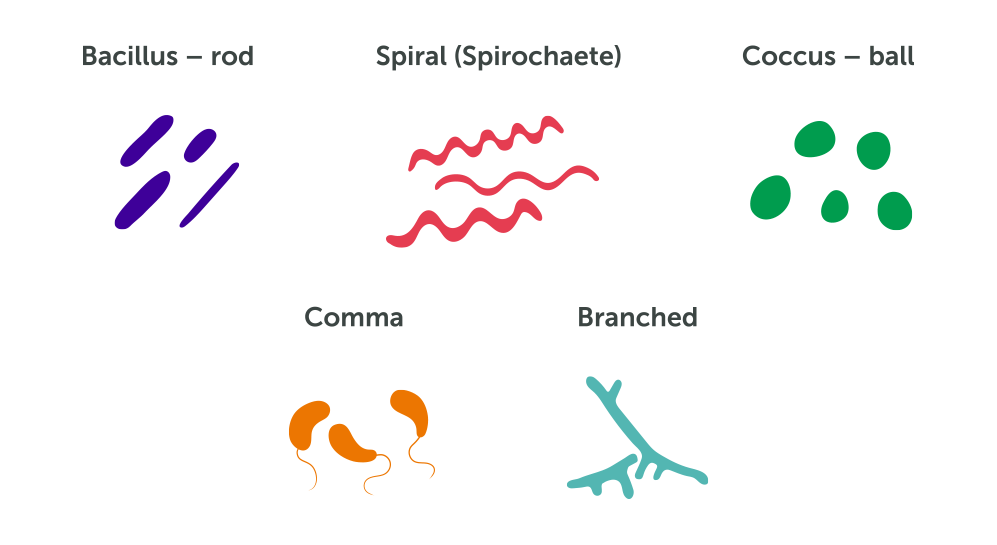
Figure 1 shows ciliate protozoa consuming bacteria.īacteria are similar in size to clay soil particles (<.2 µm) and silt soil particles (2-50 µm). A ton of microscopic bacteria may be active in each acre.” While bacteria may be small, they make up both the largest number and biomass (weight) of any soil microorganism. That is as much mass as two cows per acre. A teaspoon of productive soil generally contains between 100 million and 1 billion bacteria. 18) states that “Bacteria are tiny one-celled organisms generally 4/100,000 of an inch wide (1 µm). Used with permission and all rights reserved. Bacteria Characteristicsįigure 1: Close up view of a ciliate (protozoa) with various bacteria in the background.

Bacteria are a major class of microorganisms that keep soils healthy and productive. They actually perform very useful functions such as helping break down our food for digestion, protect against infection, and stimulate the immune system.Microbes in the soil are directly tied to nutrient recycling especially carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Next we have Nonpathogenic Bacteria, which are completely harmless. Spirilla- are spiral or corkscrew-shaped bacteria. They produce diseases such as tetanus, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, and diphtheria.ģ. They cause strep throat and blood poisoning.ĭiplo cocci- Spherical bacteria that grow in pairs. Strepto cocci- Pus-forming bacteria arranged in curved lines that resemble a string of beads. These cause boils, pustules, and abscesses. Staphylo cocci- Pus-forming bacteria that grow in clusters like a bunch of grapes. Cocci- round-shaped that appear singly or in the following groups: Pathogenic bacteria have the following classifications:ġ. Bacteria have different shapes that help identify them. These are considered harmful because they may cause disease or infection. The two primary types of bacteria are:įirst, we will look at Pathogenic Bacteria.
#BACTERIA SHAPES DEFINITION FREE#
One-celled microorganisms with both animal and plant characteristics.īacteria can exist anywhere! They can be found on skin, air, water, decayed matter, clothing, under the free edge of the nails, and body secretions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
